Scientists Grew A Beating Human Heart In The Laboratory Using Stem Cells
March 22, 2016
A team of researchers have successfully grown a beating human heart in the laboratory using stem cells.
Right now, there are 4,186 people waiting for a heart transplant in the U.S., but with a huge donor shortage not all of these patients are likely to survive. Growing transplantable hearts in a laboratory has been a long-standing dream within the medical community, and a study in the journal Circulation Research has moved it one step closer to reality.
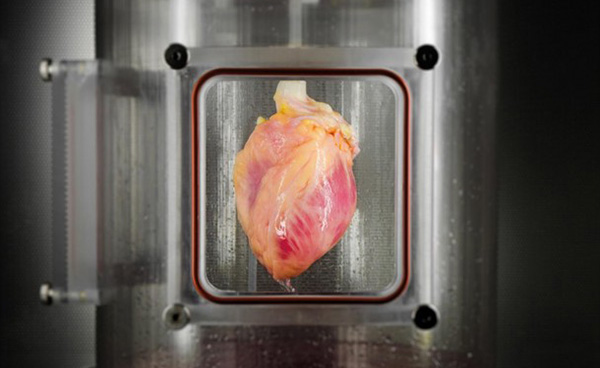
Bernhard Jank, MD, Ott Lab, Center for Regenerative Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital
Previous research has shown how 3D printers can be used to manufacture 3D heart segments using biological material. Although vacant of any actual heart cells, these structures provided the "scaffold" on which heart tissue could be grown. Now, a team from both Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Harvard Medical School has taken this scaffolding concept and combined it with stem cells for some truly spectacular results.
The main problem with heart transplants, other than a lack of donors, is that there’s a chance that the receiver’s body will reject the new organ.
For this study, 73 human hearts deemed unsuitable for transplantation were carefully immersed in solutions of detergent in order to strip them of any cells that would provoke this self-destructive response. What was left was a matrix (or “scaffold”) of a heart, complete with its intricate structures and vessels, providing a new foundation for new heart cells to be grown onto.
This is where stem cells come in.
After just two weeks, the networks of lab-grown heart cells already resembled immature but intricately structured hearts. The team gave them a burst of electricity, and the hearts actually started beating.
"Among the next steps that we are pursuing are improving methods to generate even more cardiac cells," said Jacques Guyette, a biomedical researcher at the MGH Center for Regenerative Medicine and lead author of the study, in a statement. Although this study manufactured a whopping 500 million stem cell-derived heart cells for the procedure, regrowing a whole heart would actually take "tens of billions," Guyette added.
So despite falling short of growing an entire, mature human heart in a laboratory from a patient's own cells, this is the closest anyone has come to date to reaching this goal – and that in itself is a breathtaking achievement.
via IFLScience
 Dogs Are Forced To Wear The Things They Steal — And It’s Hilarious
Dogs Are Forced To Wear The Things They Steal — And It’s Hilarious
 It Looks Like Her 2-Year-Old Ruined Her Doll — But Then Mom Shows Why It’s Perfect
It Looks Like Her 2-Year-Old Ruined Her Doll — But Then Mom Shows Why It’s Perfect
 On February 28, A Rare Planetary Parade Will Appear In The Evening Sky
On February 28, A Rare Planetary Parade Will Appear In The Evening Sky
 She Came To America With Almost Nothing — Now Her Diner Draws Crowds From Across The Country
She Came To America With Almost Nothing — Now Her Diner Draws Crowds From Across The Country
 It's Official: 'Reading Rainbow' Reboot Coming To TV And Streaming
It's Official: 'Reading Rainbow' Reboot Coming To TV And Streaming
 A Woman Stepped Up When A Little Boy’s World Was Turned Upside Down
A Woman Stepped Up When A Little Boy’s World Was Turned Upside Down
 This ‘Sloth-Like’ Lab Failed Guide Dog Training — And Found His True Calling
This ‘Sloth-Like’ Lab Failed Guide Dog Training — And Found His True Calling
 She Secretly Left Outfits For An Elderly Couple's Porch Goose… Then A Package Arrived That Left Her In Tears
She Secretly Left Outfits For An Elderly Couple's Porch Goose… Then A Package Arrived That Left Her In Tears
 Giant Sea Serpent Appears On Cabo Beach
Giant Sea Serpent Appears On Cabo Beach
 Every Night I Watch My Neighbor's Dog Go Upstairs To Bed Like This
Every Night I Watch My Neighbor's Dog Go Upstairs To Bed Like This
 Mom Realizes Why Her Daughter Poses Like A Princess — And It’s Melting Hearts
Mom Realizes Why Her Daughter Poses Like A Princess — And It’s Melting Hearts
